Truncated simplectic honeycomb
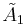 |
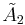 |
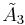 |
|---|---|---|
| Apeirogon | Trihexagonal tiling | quarter cubic honeycomb |
Yellow and cyan line segments |
With yellow and blue equilateral triangles, and red hexagons |
With yellow and blue tetrahedra, and red and purple truncated tetrahedra |
In geometry, the truncated simplectic honeycomb (or truncated n-simplex honeycomb) is a dimensional infinite series of honeycombs, based on the symmetry of the 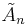 affine Coxeter group. It is given a Schläfli symbol t{3[n+1]}, and is represented by a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram as a cyclic graph of n+1 nodes with two adjacent nodes ringed. It is composed of n-simplex facets, along with all truncated n-simplices. The vertex figure of an n-simplex honeycomb is an (n-1)-simplex antiprism.
affine Coxeter group. It is given a Schläfli symbol t{3[n+1]}, and is represented by a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram as a cyclic graph of n+1 nodes with two adjacent nodes ringed. It is composed of n-simplex facets, along with all truncated n-simplices. The vertex figure of an n-simplex honeycomb is an (n-1)-simplex antiprism.
In n-dimensions, each can be seen as a set of n+1 sets of parallel hyperplanes that divide space. Each hyperplane contains the same honeycomb of one dimension lower.
In 1-dimension, the honeycomb represents a apeirogon, with alternately colored line segments. In 2-dimensions, the honeycomb represents the trihexagonal tiling, with Coxeter graph . In 3-dimensions it represents the quarter cubic honeycomb, with Coxeter graph filling space with alternately tetrahedral and truncated tetrahedral cells. In 4-dimensions its called a truncated 5-cell honeycomb, with Coxeter graph , with 5-cell and truncated 5-cell facets. In 5-dimensions its called an truncated 5-simplex honeycomb, with Coxeter graph , filling space by 5-simplex, truncated 5-simplex, and bitruncated 5-simplex facets. In 6-dimensions its called a truncated 6-simplex honeycomb, with Coxeter graph , filling space by 6-simplex, truncated 6-simplex, and bitruncated 6-simplex facets.
See also
References
- George Olshevsky, Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs, Manuscript (2006) (Complete list of 11 convex uniform tilings, 28 convex uniform honeycombs, and 143 convex uniform tetracombs)
- Branko Grünbaum, Uniform tilings of 3-space. Geombinatorics 4(1994), 49 - 56.
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- Coxeter, H.S.M. Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [1]
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10] (1.9 Uniform space-fillings)
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]